Load Pull Measurements
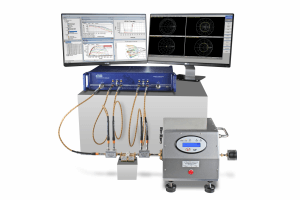 Load pull is the art of presenting a set of controlled load impedances to a device under test (DUT) while measuring a multitude of parameters at each impedance state. By systematically varying the impedance, it is possible to characterize the performance of a device and design the ideal matching network for optimum realistic large-signal operating conditions.
Load pull is the art of presenting a set of controlled load impedances to a device under test (DUT) while measuring a multitude of parameters at each impedance state. By systematically varying the impedance, it is possible to characterize the performance of a device and design the ideal matching network for optimum realistic large-signal operating conditions.
Vector-receiver load pull, or VNA-based load pull, is a modern and efficient methodology for load pull measurements. Low-loss couplers are placed between the tuners and device-under-test and are connected to the receivers of a VNA, such as a Copper Mountain Technologies’ Cobalt VNA. Doing so allows the a- and b-waves to be measured at the DUT reference plane in real-time, presenting vector information not normally made available through traditional power-meter load pull techniques. Vector-receiver load pull allows the direct measurement of actual impedances presented to the DUT without any assumptions of pre-characterized tuner positioning or losses. The delivered input power is derived from the a- and b-waves with incredible accuracy, which results in properly- defined power added efficiency. Output powers at each frequency, fundamental and multiple harmonics, are made available, as are multi-tone carrier and intermodulation powers. Time-domain NVNA measurements are easily implemented using appropriate hardware. Learn more about performing load pull measurements with Maury Microwave and Copper Mountain Technologies in the solutions brochure here.
Copper Mountain Technologies’ VNAs compatible with Maury Microwave Load Pull Solutions include:


