The trace calculator performs mathematical processing of measurement data according to the specified algebraic equation and displays the result on the calculator trace. The analyzer channel is the scope of the calculator: the source data refers to one channel, and the calculator trace is displayed in the channel window together with the channel measurement traces. The calculator can take source data from the following processing stages in the analyzer channel (see figure below):
•S-parameters.
•Absolute measurements (receivers Rn, An, Bn).
•Raw data of trace or memory (Trn.Src, Trn.Mem.Src).
•Mathematically processed trace or memory data before formatting (Trn, Trn.Mem).
•Displayed trace or memory data (Trn.Disp, Trn.Mem.Disp).
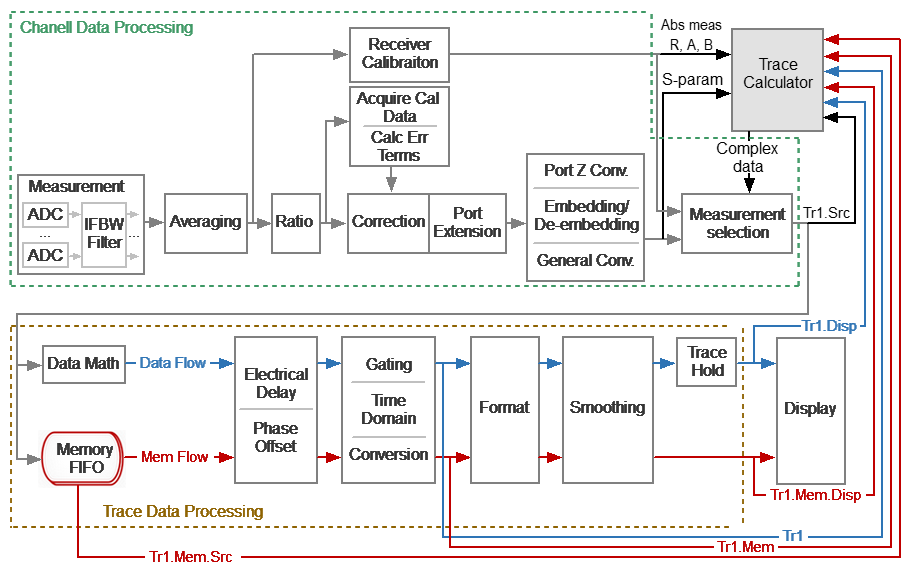
Data Processing Flowchart
One or more calculator traces calculated from different algebraic expressions can be added to a channel. Calculator traces are among the 16 maximum possible traces in the channel.
note |
If an S-parameter or absolute measurement is selected as an argument in the expression, and the corresponding trace is not present in the channel, then the analyzer will automatically measure this parameter by sending a stimulus to the appropriate ports. |
The calculator trace is drawn using frequency measurement points. Each frequency point of the calculator trace is the result of a mathematical operation on the data measured at this frequency point. The source arguments of the calculator equation are complex quantities. If the arguments are taken after formatting in rectangular coordinates, then they are brought into complex form by adding a zero imaginary part. The result of the equation calculation is also a complex value that is displayed on the calculator trace according to the selected format. The active trace is converted to the calculator trace and updates in real time when equation entry is completed. Since the data processing flowchart is similar for all traces, all operations that are available for all traces are applicable to the calculator trace, including memory operations, time domain operations, and others.
The calculator can operate in two modes: basic or advanced. In the basic mode, the equation is selected from a limited list of preset equations, and the number of arguments is also limited. The advanced mode uses an arbitrary custom equation that can use a great number of mathematical functions and an unlimited number of arguments.
To use the calculator in each mode, see Basic Mode and Advanced Mode.
Turning on the Calculator
|
To turn the calculator on, use the following softkeys: Measurement > Calculator... A calculator window will appear on the screen. |
The calculator can be enabled using the Trace Manager:
|
|