The default reference impedance of a port is equal to the reference impedance of the connectors (50 or 75 Ω). But in the process, it is often required to measure DUT with arbitrary resistance (See example in the figure below), not equal to the reference impedance of a port. In this case, it is possible to convert the reference impedance to an arbitrary impedance value using the program.
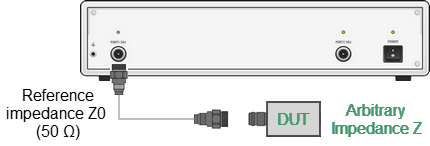
Measurement of DUT with Arbitrary Impedance
Port reference impedance conversion is a function that mathematically converts the matrix of S-parameters measured at the reference impedance of port Z0 to the matrix of S-parameters measured at an arbitrary impedance of port Z1 (See figure below). The function is also referred to as the renormalization transformation of S-parameters.
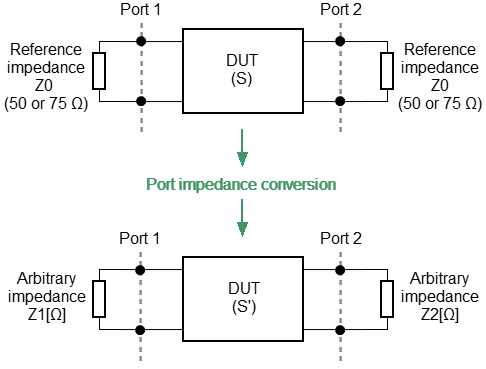
Port Reference Impedance Conversion
note |
The source value of the Z0 port reference impedance (commonly 50 Ω) is defined in the process of the calibration. It is determined by the characteristic impedance of the calibration kit and its value is entered as described in System Impedance Z0. |
|
To enable/disable the port reference impedance conversion function, use the following softkeys: Analysis > Fixture Simulator > Port Z Conversion > Port Z Conversion [ON | OFF] |
|
To enter the value of the simulated impedance of Port n, use the Port 1 Z0 and Port 2 Z0 softkeys. |
|
|