This section describes ways to optimize the measurement:
•Narrowing the IF bandwidth of measurement receivers increases the signal-to-noise ratio and extends the dynamic range of measurements. This increases the value of the sweep time. For a detailed description see IF bandwidth.
•Averaging allows to increase the signal-to-noise ratio and extend the dynamic range of the measurements. Averaging does not increase the value of the sweep time, but the averaging result is complete after N sweeps, where N is an averaging factor. For a detailed description see Averaging.
•Smoothing does not change the dynamic range of the measurements, but reduces the noise emissions of the signal. For a detailed description see Smoothing.
The figure below shows an example of applying different filtering methods to the signal: the IF bandwidth is reduced by a factor of 10, averaging factor is set to 100, and smoothing is applied with an aperture of 2%.
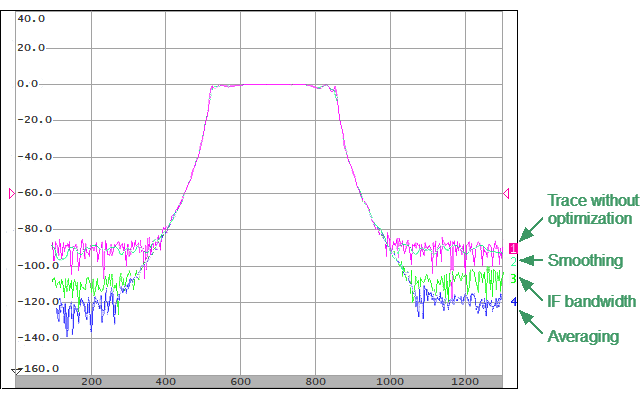
Example of the Application of Different Measurement Optimization