A model of a calibration standard presented as an equivalent circuit is used for determining S-parameters of the standard. The model is employed for standards of OPEN, SHORT, LOAD, THRU types.
A one-port model is used for the standards OPEN, SHORT and LOAD (See Full One-Port Calibration). This is shown in the figure below.
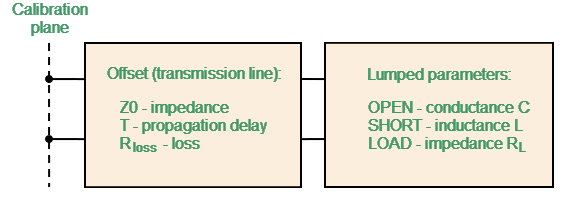
One-port Standard Model
The two-port model is used for the standard THRU (See figure below).
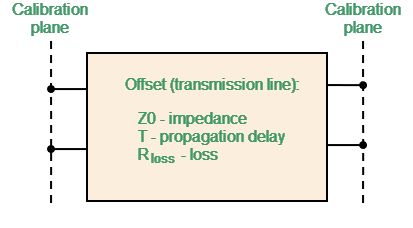
Two-port Standard Model
The description of the numeric parameters of an equivalent circuit model of a calibration standard is shown in the table below.
Parameters of the Calibration Standard Equivalent Circuit Model
Parameter (as in the Program) |
Parameter Definition |
|---|---|
Z0 (Offset Z0) |
The characteristic impedance of the transmission line [Ω], serving as the offset. For the coaxial line specified real value of characteristic impedance, usually equal to 50 Ω or 75 Ω. |
T (Offset Delay) |
The offset delay. It is defined as one-way propagation time (in seconds) from the calibration plane to the circuit with lumped parameters or to the other calibration plane. Each standard delay can be measured or mathematically determined by dividing the exact physical length by the propagation velocity. |
Rloss (Offset Loss) |
The offset loss in one-way propagation due to the skin effect [Ω/sec]. The loss in a coaxial transmission line is determined by measuring the delay T [sec] and loss L [dB] at 1 GHz frequency. The measured values are used in the following formula:
|
C (C0, C1, C2, C3) |
The fringe capacitance of an OPEN standard, which causes a phase offset of the reflection coefficient at high frequencies. The fringe capacitance model is described as a function of frequency, which is a polynomial of the third degree: , where — frequency [Hz], C0…C3 — polynomial coefficients. Units: C0[F], C1[F/Hz], C2[F/Hz2], C3[F/Hz3]. |
L (L0, L1, L2, L3) |
The residual inductance of a SHORT standard, which causes a phase offset of the reflection coefficient at high frequencies. The residual inductance model is described as a function of frequency, which is a polynomial of the third degree: , where — frequency [Hz], L0…L3 — polynomial coefficients. Units: L0[H], L1[H/Hz], L2[H/Hz2], L3[H/Hz3]. |
Minimum and Maximum Frequency (Fmin, Fmax) |
The minimum and maximum standard operating frequency in the coaxial. Used for a calibration using several calibration standards, each of which does not cover entire frequency range. |