The DUT is connected to the Analyzer ports. The Analyzer emits a test signal (stimulus) out of a source port. Simultaneously, all ports of the Analyzer are receivers. The frequency of the test signal changes in the specified range discretely from point to point. At each frequency point, the Analyzer simultaneously measures the magnitude and phase of the signal transmitted through and reflected from the DUT. These are compared with the magnitude and phase of the incident test signal. The Analyzer calculates the S-parameters of the DUT at each frequency point based on this comparison (See figure below).
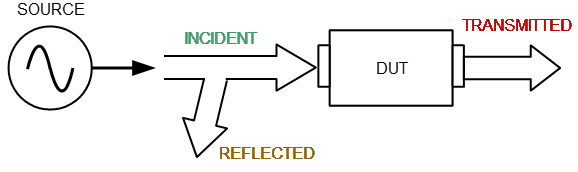
S-parameter definition
The S-parameter is a relation between the complex magnitudes of two waves:
Provided that the incoming wave is zero on all ports except the port n, where m, n denote the DUT port number.
For a two-port DUT the Analyzer measures the full scattering matrix:
For the measurement of S11, S21 parameters, test Port 1 will operate as a signal source. The incident and reflected waves will be measured by Port 1. The transmitted wave will be measured by Port 2.
For the measurement of S12, S22 parameters, test Port 2 will operate as a signal source. The incident and reflected waves will be measured by Port 2. The transmitted wave will be measured by Port 1.
For a four-port DUT the Analyzer measures the full scattering matrix:
When a stimulus is applied to one of the test ports, the Analyzer measures four S-parameters, which constitute one column in the S-parameter matrix. To have the full scattering matrix, the four-port Analyzer applies a stimulus to all the four test ports one after another. You do not need to change the connection of the DUT to the Analyzer.