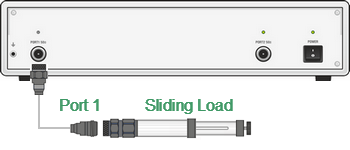
In SOLT calibrations, it is possible to employ a Sliding Load calibration standard instead of a fixed one. The use of the SLIDING LOAD standard allows for significant increase in calibration accuracy at high frequencies compared to the FIXED LOAD standard.
The Sliding Load calibration involves a series of measurements in different positions of the sliding element to compensate for reflection from the dissipation component.
Sliding Load Calibration
To activate the Sliding Load calibration algorithm, the selected calibration kit should contain a calibration standard of SLIDING LOAD type, and it should be assigned to the "Load" class of the corresponding port. Calibration standard editing and class assignment are further described in detail in Calibration Standard Definition.
If a calibration kit contains a SLIDING LOAD, the menu selection for the load will lead to a submenu for selection of the various sliding load positions.
The Sliding Load calibration involves a series of measurements in different positions of the sliding element. The minimum number of measurements is 5, the maximum number of measurements is 8.
...
|
In the main menu of one-port or two-port calibration, the Load softkey will open the Sliding Load menu (if the above-mentioned condition is met). Connect the SLIDING LOAD to a selected test ports and perform a series of measurements in different positions of the sliding element clicking the Position 1, Position 2 … Position 8 softkeys. |
note |
The Sliding Load calibration is not suitable for low frequencies. To eliminate this limitation, use a FIXED LOAD standard in the lower part of the frequency range. For combined calibration with SLIDING and FIXED LOADS, use the procedure of standard subclasses assigning (See Sliding Load Calibration Example Using Subclasses). |