The Polar format is used to display the amplitude and phase of the reflection coefficient () when measuring Sii (where a value from 1 to N is taken, N is a number of Analyzers). The complex reflection coefficient values are displayed on the polar diagram in the complex plane. The complex plane is formed by the real horizontal and the imaginary vertical axes. The grid lines correspond to points of equal amplitude and phase (See figure below).
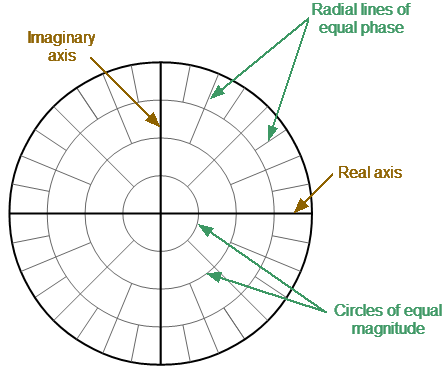
Polar format
note |
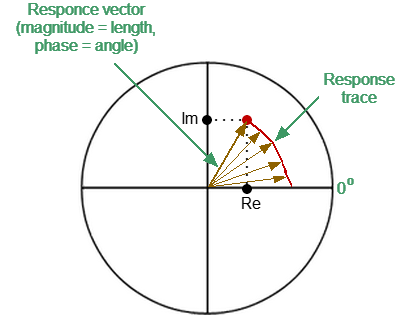
On circular diagrams (Polar and Smith chart), any point of the trace can be defined in the following two ways (See figure below): •Coordinates of the point (Re, Im) on the real and imaginary coordinate axes. •Parameters of the vector directed to the point from the center of the diagram. The length of this vector is equal to the response amplitude, and the angle between the vector and the positive part of the real coordinate axis is equal to the phase of the response. The angle is calculated counterclockwise.
|
note |
Traces on all types of Smith chart and polar format are the same, the analyzer replaces the base grid and default marker format when switching formats. |
The Polar format diagram with the characteristic points is shown in the figure below.
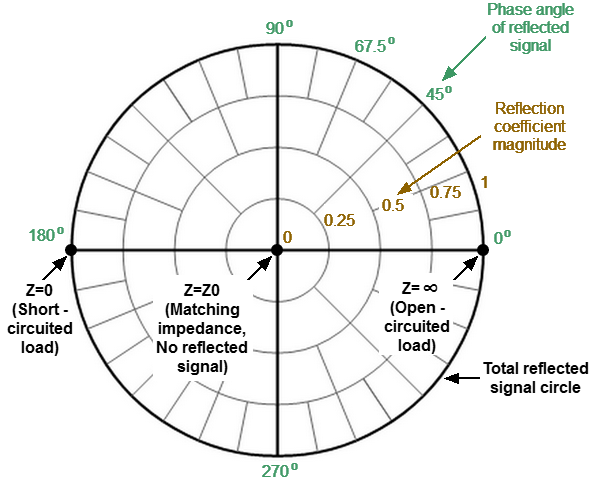
Properties of Polar format
Basic properties of the Polar format:
•The center of the diagram corresponds to the reflection coefficient = 0 (reference impedance Z0 on the input test port of the DUT when measuring Sii, matched circuit, no reflection).
•The outer circle of the diagram corresponds to the reflection coefficient = 1 (|Sii| = 1, unmatched circuit, total reflection).
•Points with the same amplitude are located on a circle with the center coinciding with the center of the diagram.
•Points with the same phase are located on a line starting from the center.
•At the rightmost point of the horizontal axis, the impedance has an infinitely large value (Open circuited load).
•At the leftmost point of the horizontal axis, the impedance value is zero (Short circuited load).
The polar graph does not have a frequency axis, so frequency is indicated by markers. There are three types of polar formats corresponding to the data displayed by the marker; the traces remain the same for all the format types (See table below).
Format Type Description |
Label |
Data Displayed by Marker |
Measurement Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
Linear Magnitude and Phase |
Polar (Lin) |
S-parameter linear magnitude |
Dimensionless value |
S-parameter phase |
Degree (°) |
||
Logarithmic Magnitude and Phase |
Polar (Log) |
S-parameter logarithmic magnitude |
Decibel (dB) |
S-parameter phase |
Degree (°) |
||
Real and Imaginary Parts |
Polar (Re/Im) |
S-parameter real part |
Dimensionless value |
S-parameter imaginary part |
Dimensionless value |
The format for each trace of the channel can be selected individually. The trace must be activated before setting the format (See Active Trace Selection).
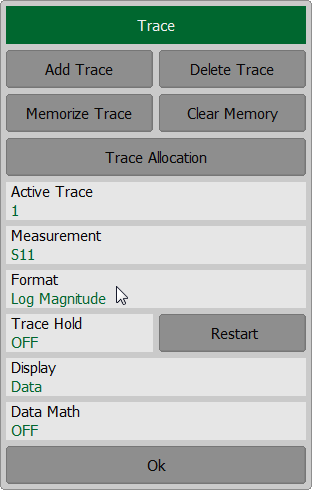
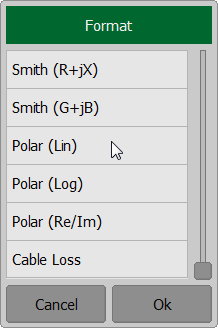
To set the trace display format use the following softkey Trace. In the Trace dialog select the required trace from Active Trace and click on Format softkey. Then select the required format in the Format dialog.
|
note |
The display format can be set using the mouse (See Display Format Setting). |