The Analyzer emits a test signal (stimulus) out of a port connected to the DUT. The frequency of the test signal changes in the specified range discretely from point to point. At each frequency point, the Analyzer simultaneously measures the magnitude and phase of the signal transmitted through and reflected from the DUT. These are compared with the magnitude and phase of the incident test signal. The Analyzer calculates the S-parameters of the DUT at each frequency point based on this comparison (See figure below).
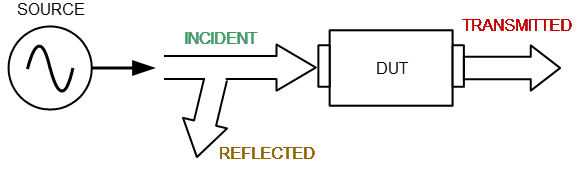
S-parameter terms
The S-parameter is a relation between the complex magnitudes of two waves:
Providing the , except = 0, where denote the DUT port number.
In accordance with the measurement plan, the Analyzer performs a frequency sweep in one direction in a specified frequency range. Then, if needed, the Analyzer performs a frequency sweep in reverse direction in a specified frequency range. The frequency changes discretely, according to the number of measuring points specified. S-parameters of the DUT are measured for each measuring point.
1-port Analyzer has one measurement port which operates as a signal source and as a reflected signal receiver. That is why the Analyzer only allows for the measurement of the S11 parameter.